Chapter 20: DNA Technology and Genomics
Key Terms
1.Recombinant DNA = molecule of DNA with portions from different sources
2. Genetic Engineering = manipulation of genes for various purposes and applications
3. Gene Cloning = producing multiple copies of a certain gene
4. Biotechnology = manipulating living organisms or their components to produce useful products
5. Restriction Enzyme = degradative enzyme that can recognize and cut up DNA that is foreign
6. Restriction Site = specific sequence on a strand of DNA that is recognized by the restriction enzyme
7. Restriction Fragments = segment of DNA arising from the cutting of DNA by a restriction enzyme
8. DNA Ligase = enzyme that links restriction fragments together
9. Sticky End = the single stranded end of a double stranded DNA restriction fragment
10. Cloning Vector = used to transfer DNA. In genetic engineering, it is often a plasmid that moves recombinant DNA from the test tube back into a cell.
11. Nucleic Acid Hybridization = describes how a complementary sequence on another nucleic acid molecule base pairs with a specific gene
12. Nucleic Acid Probe = labeled single stranded nucleic acid molecule that tags a specific nucleotide sequence in a sample. It hydrogen bonds to the complementary sequence wherever it occurs. This can be visually detected by labeling the probe with a radioactive isotope.
13. Denaturation = occurs under extreme conditions of pH, salt concentration, and temperature. These conditions make a protein unravel and lose its active conformation, and in DNA the two strands of the double helix separate.
14. Genomic Library = thousands of DNA segments from a genome, each one is carried by a phage, plasmid, or other cloning vector
15. Complementary DNA (cDNA) = DNA molecule made in vitro using mRNA as the template and reverse transcriptase as the enzyme (obtained from retroviruses). Lacks the introns present in the DNA of the genome, but matches to a specific gene.
16. cDNA Library = limited gene library of complementary DNA (without introns); only the genes transcribed in the cells that were examined
17. Expression Vector = cloning vector that contains the necessary prokaryotic promoter before a restriction site where a eukaryotic gene can be inserted
18. Yeast Artificial Chromosomes (YACs) = vector that combines the vital parts of a eukaryotic chromosome with foreign DNA
19. Electroporation = technique to introduce recombinant DNA into cells by the application of a short electrical pulse to a solution with the cells. This creates temporary holes in the plasma membranes so that the DNA can enter.
20. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) = method for amplifying DNA in vitro by incubating with special primers Polymerase molecules and nucleotides for a certain amount of time
21. Gel Electrophoresis = method to separate nucleic acids or proteins based on size and electrical charge, measures the molecule’s rate of movement through an electrical field in a gel
22. Southern Blotting = hybridization method allowing the determination of the presence of certain nucleotide sequences in a sample of DNA
23. Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) = the differences in DNA sequence on homologous chromosomes that result in different patterns of restriction fragment lengths (DNA segments resulting from restriction enzyme treatment); acts as genetic markers for making linkage maps
24. Human Genome Project = collaborative effort of researchers around the world to map and sequence the DNA of the entire human genome. Sequenced the genomes of many other organisms as well, so as to better understand the human genome.
25. Linkage Map = genetic map based on frequencies of recombination between markers during the crossing over of homologous chromosomes
26. Physical Map = genetic map showing the actual physical distances between genes or genetic markers, usually as the number of base pairs along the molecule of DNA
27. Bacterial Artificial Chromosome (BAC) = an artificial version of a bacterial chromosome, can carry 100,000 – 500,000 base pairs
28. Celera Genomics = founded by molecular biologist J. Craig Venter who devised an alternative approach to the sequencing of whole genomes. Sequenced the genomes of many organisms (including Drosophila melanogaster) just like the Human Genome Project.
29. Genomics = study of whole sets of genes and the interactions between them
30. in vitro Mutagenesis = technique to find the function of a gene. Specific changes into the sequence of a cloned gene are introduced and a mutated gene is reinserted to study the phenotype of the resulting mutant.
31. RNA Interference (RNAi) = method to silence the expression of selected genes in nonmammalian organisms. Uses synthetic double stranded RNA molecules complementary to the sequence of a particular gene to trigger the breakdown of the gene’s messenger RNA.
32. DNA Microarray Assays = method to measure and detect the expression of a large number of genes at a time. Small amounts of many single stranded DNA fragments representing different genes are fixed on a glass slide. These fragments are tested for hybridization with cDNA.
33. Proteomics = study of the full protein sets encoded by genomes
34. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) = variation of one base pair within the genome sequence
35. Gene Therapy = altering genes of a person that has a genetic disease
36. DNA Fingerprint = an individual’s distinctive set of DNA restriction fragments, detected by electrophoresis and nucleic acid probes
37. Transgenic = plant or animal with a genome that contains a gene from another organism (different or same species)
38. Ti Plasmid = plasmid of a tumor-inducing bacterium that incorporates a segment of its DNA into the host chromosome of a plant
39. Bioremediation – use of living organisms to detoxify polluted and degraded ecosystems
40. Genetically Modified Organisms (GM) = organism that has one or more genes incorporated artificially, also known as an transgenic organism
2. Genetic Engineering = manipulation of genes for various purposes and applications
3. Gene Cloning = producing multiple copies of a certain gene
4. Biotechnology = manipulating living organisms or their components to produce useful products
5. Restriction Enzyme = degradative enzyme that can recognize and cut up DNA that is foreign
6. Restriction Site = specific sequence on a strand of DNA that is recognized by the restriction enzyme
7. Restriction Fragments = segment of DNA arising from the cutting of DNA by a restriction enzyme
8. DNA Ligase = enzyme that links restriction fragments together
9. Sticky End = the single stranded end of a double stranded DNA restriction fragment
10. Cloning Vector = used to transfer DNA. In genetic engineering, it is often a plasmid that moves recombinant DNA from the test tube back into a cell.
11. Nucleic Acid Hybridization = describes how a complementary sequence on another nucleic acid molecule base pairs with a specific gene
12. Nucleic Acid Probe = labeled single stranded nucleic acid molecule that tags a specific nucleotide sequence in a sample. It hydrogen bonds to the complementary sequence wherever it occurs. This can be visually detected by labeling the probe with a radioactive isotope.
13. Denaturation = occurs under extreme conditions of pH, salt concentration, and temperature. These conditions make a protein unravel and lose its active conformation, and in DNA the two strands of the double helix separate.
14. Genomic Library = thousands of DNA segments from a genome, each one is carried by a phage, plasmid, or other cloning vector
15. Complementary DNA (cDNA) = DNA molecule made in vitro using mRNA as the template and reverse transcriptase as the enzyme (obtained from retroviruses). Lacks the introns present in the DNA of the genome, but matches to a specific gene.
16. cDNA Library = limited gene library of complementary DNA (without introns); only the genes transcribed in the cells that were examined
17. Expression Vector = cloning vector that contains the necessary prokaryotic promoter before a restriction site where a eukaryotic gene can be inserted
18. Yeast Artificial Chromosomes (YACs) = vector that combines the vital parts of a eukaryotic chromosome with foreign DNA
19. Electroporation = technique to introduce recombinant DNA into cells by the application of a short electrical pulse to a solution with the cells. This creates temporary holes in the plasma membranes so that the DNA can enter.
20. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) = method for amplifying DNA in vitro by incubating with special primers Polymerase molecules and nucleotides for a certain amount of time
21. Gel Electrophoresis = method to separate nucleic acids or proteins based on size and electrical charge, measures the molecule’s rate of movement through an electrical field in a gel
22. Southern Blotting = hybridization method allowing the determination of the presence of certain nucleotide sequences in a sample of DNA
23. Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) = the differences in DNA sequence on homologous chromosomes that result in different patterns of restriction fragment lengths (DNA segments resulting from restriction enzyme treatment); acts as genetic markers for making linkage maps
24. Human Genome Project = collaborative effort of researchers around the world to map and sequence the DNA of the entire human genome. Sequenced the genomes of many other organisms as well, so as to better understand the human genome.
25. Linkage Map = genetic map based on frequencies of recombination between markers during the crossing over of homologous chromosomes
26. Physical Map = genetic map showing the actual physical distances between genes or genetic markers, usually as the number of base pairs along the molecule of DNA
27. Bacterial Artificial Chromosome (BAC) = an artificial version of a bacterial chromosome, can carry 100,000 – 500,000 base pairs
28. Celera Genomics = founded by molecular biologist J. Craig Venter who devised an alternative approach to the sequencing of whole genomes. Sequenced the genomes of many organisms (including Drosophila melanogaster) just like the Human Genome Project.
29. Genomics = study of whole sets of genes and the interactions between them
30. in vitro Mutagenesis = technique to find the function of a gene. Specific changes into the sequence of a cloned gene are introduced and a mutated gene is reinserted to study the phenotype of the resulting mutant.
31. RNA Interference (RNAi) = method to silence the expression of selected genes in nonmammalian organisms. Uses synthetic double stranded RNA molecules complementary to the sequence of a particular gene to trigger the breakdown of the gene’s messenger RNA.
32. DNA Microarray Assays = method to measure and detect the expression of a large number of genes at a time. Small amounts of many single stranded DNA fragments representing different genes are fixed on a glass slide. These fragments are tested for hybridization with cDNA.
33. Proteomics = study of the full protein sets encoded by genomes
34. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) = variation of one base pair within the genome sequence
35. Gene Therapy = altering genes of a person that has a genetic disease
36. DNA Fingerprint = an individual’s distinctive set of DNA restriction fragments, detected by electrophoresis and nucleic acid probes
37. Transgenic = plant or animal with a genome that contains a gene from another organism (different or same species)
38. Ti Plasmid = plasmid of a tumor-inducing bacterium that incorporates a segment of its DNA into the host chromosome of a plant
39. Bioremediation – use of living organisms to detoxify polluted and degraded ecosystems
40. Genetically Modified Organisms (GM) = organism that has one or more genes incorporated artificially, also known as an transgenic organism
Dolly

From: http://www.prism.gatech.edu/~gh19/b1510/dolly.gif
The female sheep, Dolly, (left) is the first mammal to be successfully cloned.
Recombinant Mice

From: http://www.biology.iupui.edu/biocourses/N100H/images/15ghmice.gif
The mouse on the right is much larger than the one on the left because it has been injected with a gene that produces growth hormone.
Gel Electrophoresis
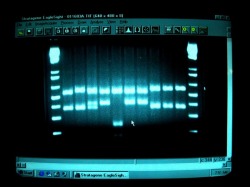
From: ttp://oceanexplorer.noaa.gov/explorations/03bio/logs/sept10/media/lasonolide3_600.jpg
Gel electrophoresis is commonly used to get the DNA fingerprint of an organism. Applications include forensics (determining the guilt of a suspect) and domestic issues (paternity testing).
Ethics

From: http://www.cartoonstock.com/newscartoons/cartoonists/mba/lowres/mban1450l.jpg
Many people feel that the concept of genetic engineering is similar to playing God because its goal is to perfect defects. Some feel that the human race has taken technology too far, others feel that this technology enhances life and should be welcomed.
